Database design
Overview
- Online transaction processing (OLTP) databases, in which users are concerned with creating, reading, updating, and deleting records, should be normalized. CRUD
- Online analytical processing (OLAP) databases which favor analysis and reporting works better with a degree of denormalization, we’re worried about the speend of calculation/fetching data and the data doesn’t really change that much. Also not a lot of inserts.
- Composite key is a primary key with two cols to identify a record uniquely.
- Foreign key it references the primary key in another table. They don’t have to be unique and can be NULL too. Helps with referential integrity.
- Transitive functional dependencies changing a non-key column, might cause any of the other non-key columns to change
- Cardinality number of elements that interact between two tables.
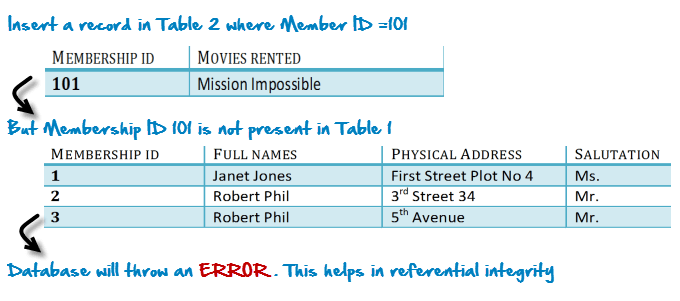
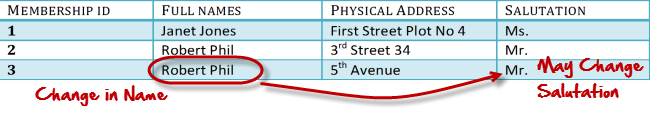
Normalisation
Without normalization all the data is in one table and kind of redundant.
1NF
- Each table cell should contain a single value.
- Each record needs to be unique.
2NF
- Be in 1NF
- Single col primary key (no composite keys). So partition table or introduce a new primary key.
- No partial dependencies.
3NF (Standard)
- Be in 2NF
- No transitive functional dependencies. May need to partition and add foreign keys.
- At the very least should be in this form.
There’s a BCNF (3.5) and then it goes up to 6NF but nobody really normalizes it beyond 3NF.
Relationships
- 1-1
- 1-Many: Add primary key in the other tables making it a foreign key.
- Many-Many: In the scenario of students and classes. The way it is implemented is it involves breaking it into two 1-Many relationships.
Many-Many
Create a new “entity” (table) to go in between the Many-Many. AKA associative entity.
Best practices
-
Stored procedures: Makes development more clean. Will write a completely new post for this.
-
https://www.guru99.com/database-normalization.html

